No matter the size of your organization, chances are you will eventually have to deal with a security incident. When this happens, the best way to understand what went wrong is to access your system logs. If they are incomplete or inaccurate (or, even worse, if they don’t exist), you won’t be able to investigate further.
In this article, we will cover some of the best practices to guarantee a proper audit log management process, including how to track events, centralize audit logs, and do log analysis. So, let’s get started!
About Audit Logging
Audit logs or audit trails are a record of all activities and events within a system. This includes attempts to log on, network connections, and file data access.
The purpose of keeping audit logs is to monitor how your company’s sensitive data is treated. Through an audit logs record, for example, you can see whether a system has been changed in any way and detect any threats to its integrity (as you’ll have access to events and timestamps). In other words, your log data serves as a comprehensive record that gives you a transparent trail of who accessed what, when, and any modifications made.
What’s more, audit logs are also typically required when you have to undergo an outside security audit. By maintaining a log of access changes, you can demonstrate accountability and provide a historical record of who had access to specific resources or made alterations to permissions.
Collecting Audit Logs
Audit logs can track several types of system events and activities. For instance, here are some common types of audit logs:
- Access control: Audit logs capture whether there have been any changes to permissions and access rights. For example, you can see alterations in user permissions, access levels, and rights within a system or across databases.
- User activity: User activity logging includes the record of all actions taken by individuals interacting with a system, such as identities, login and logout, timestamps, and a wide range of actions and operations like file modifications, database queries, system configurations, application usage, and more.
- System events: Logs also collect information about system events like shutdown, startup, and performance issues. This encompasses details such as CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, network latency, and other performance metrics (and, of course, any abnormalities associated with them). Errors, warnings, and alerts are also logged.
- Security events: Security events encompass a broad spectrum of activities, such as intrusion attempts (failed login attempts, brute-force attacks, or suspicious activities), malware, viruses, or other malicious software triggers, security violations, and anomalies like unusual traffic.
- Data access: Logs related to data access focus on recording instances of users accessing, modifying, or interacting with sensitive information within the system. This includes user access log data, data modification records, and permission changes.
- Configuration changes: Lastly, configuration change logs document alterations to system settings, software configurations, network settings, and other parameters that impact functionality and security (such as software updates, network configuration changes, and system setting adjustments).
Audit Logs and Log Data Best Practices
Audit logs are the cornerstone of robust security. Considering we live in an era marked by increasing cybersecurity threats and stringent regulatory requirements, the effective management and utilization of these logs and their data are pivotal in safeguarding sensitive information, ensuring compliance, and detecting potential security breaches. So, let’s see some best practices for log management.
#1: Establish Your Logging Policies
The first step towards effective logging is to have strong policies. These policies will be the foundation of your entire forensic analysis, so they need to cover all aspects of logging – from historical log data to all relevant events, user accounts, and changes.
Policies are crucial for ensuring comprehensive coverage for forensic analysis, security monitoring, and compliance requirements. When you design yours, make sure you include:
- Define what events and activities will be logged. This could include user logins and logouts, system startups and shutdowns, software installations or updates, file access and modifications, network activity, and security-related incidents.
- Establish clear guidelines on how long different types of logs will be retained (compliance regulations often dictate specific retention periods).
- Clearly outline who has access to the logs and who is responsible for maintaining and monitoring them.
- Specify measures to ensure the integrity and protection of log data (for example, using encryption, backup procedures, hash functions, or digital signatures).
- Ensure that the logging policies align with industry standards and legal regulations.
- Provide training and awareness programs to employees to ensure they understand the importance of logging policies, their role in compliance, and the impact of their actions on the security and integrity of the system.
#2: Capture The Critical Questions
There are three main questions that can help you create the most comprehensive audit logs. These are: What happened? What was affected?, and when did it happen?. All of these should also be linked to a unique user or log ID.
The first question, What happened?, should cover all the essential information about the event or message. The What was affected? question refers to the relevant systems (or IP addresses) that were involved in the event. Lastly, the When did it happen? question logs the precise time an event took place. This timestamp should always be synchronized with a centralized time source and have all relevant endpoints.
#3: Use An Appropriate Audit Logging Tool
Your choice of logging tool can significantly impact your organization’s capability to collect, store, and analyze log data efficiently. A good audit logging tool should align with your specific needs and be able to handle the volume and complexity of log data. Ideally, it should also provide real-time monitoring and facilitate comprehensive analysis for security, compliance, and operational insights (more on this below).
Some important considerations when picking a logging tool include scalability, performance, flexibility, and query capabilities. In other words, the tool should be capable of handling large volumes of log data and scaling alongside your organization’s growth. It should also have real-time monitoring capabilities and provide customizable options for log collection and analysis. And, of course, an effective logging tool should offer robust search and query functionalities to navigate through log data and give quick access to specific information during forensic investigations or troubleshooting.
#4: Centralize Audit Logs
Centralizing audit logs is all about aggregating log data from various sources and systems into a single, unified location. The goal? To streamline analysis, monitoring, and management. By consolidating logs from diverse systems, applications, and devices, you can gain a complete view of user activities, system events, security incidents, and performance metrics.
Simplify Audit Log Management with Uniqkey
Centralizing audit logs is essential, but it can also be complex. Uniqkey provides IT teams with a solution that simplifies and streamlines the management of audit trails. Our centralized dashboard presents audit logs from various systems in a clear and intuitive format. This enables IT admins to:
- Quickly identify and investigate security incidents: Easily filter and pinpoint suspicious activities, speeding up investigations.
- Demonstrate compliance with ease: Generate audit reports aligned with regulatory requirements in just a few clicks.
- Proactively monitor user activities: Get an immediate overview of system access patterns to detect potential risks.
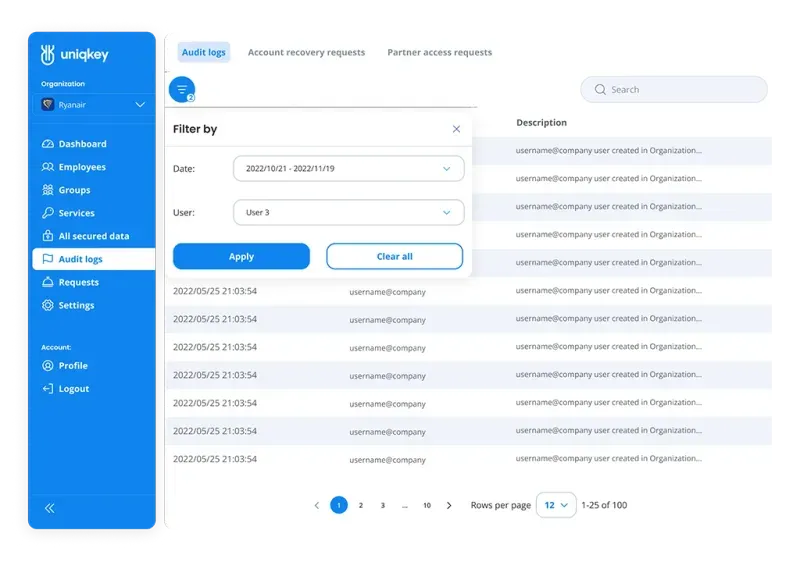
🔥Upgrade your audit log capabilities with Uniqkey – Book a demo today!
A centralized approach can also significantly simplify the task of responding to security incidents, as certain anomalies, threats, and patterns might be missed when logs are dispersed across multiple locations. What’s more, centralized logs facilitate more efficient audits, support forensic investigations, and aid in meeting regulatory requirements by ensuring all relevant data is easily accessible and organized.
#5: Use a Fail-Safe Option
There are two possible ways to keep logs. You either use a “fail open” option or you implement a “fail safe” one. The first can help you keep operating no matter what happens, but your system won’t be protected during that time.
A fail-safe option can protect your assets and allow you access to your operating system even when you suffer a disruption. Some common fail-safe ideas include frequent backups and redundant storage. Other options are high-availability systems, disaster recovery plans, fault-tolerant architectures, and automated alert systems. All of these can help you mitigate risks and ensure business continuity.
#6: Use Automated Tools for Collection and Analysis
Trying to log data and analyzing it manually can be extremely time-consuming. What’s more important, this technique is susceptible to human error, especially if you have to deal with large amounts of information.
A better way to do log management is to use automated tools that can discover suspicious activities and anomalies as soon as they happen. Automated tools collect logs in real-time or on a scheduled basis and eliminate the need for manual retrieval – saving time and ensuring that no critical data is missed.
Conclusion
Audit log best practices serve not only as a retrospective view of system activities but also as a proactive shield against potential security threats, compliance vulnerabilities, and operational inefficiencies.
By establishing meticulous logging policies, choosing appropriate tools, and centralizing log data, your IT team fortifies your organization’s ability to detect anomalies, respond to incidents, and comply with regulatory standards.
Are you looking for an easy way to give your IT admins complete visibility and centralized control of all accounts and employee access permissions? If you need an easy way to simplify your password management and reduce password-based risk, we can help. Uniqkey is an all-in-one tool trusted by leading businesses across Europe. Learn more about Uniqkey’s password management solution and raise your company-wide security today!


