Although companies worldwide use email as a primary form of communication, it remains a vulnerable method that can put your operations at risk. This is why, no matter if you’re a small business or a massive enterprise, email security best practices must never be neglected.
This article will show you how to secure your data privacy and prevent phishing attacks. We’ll start with a few quick definitions and then move on to ten proven best practices to secure all your communications.
Why Email Security Matters?
Emails are often targeted by cyber-criminals who want to access sensitive and confidential information. Let’s see an example.
In 2014, some of the top Sony Pictures executives (including its CEO Michael Lynton) received an email from Apple asking to share ID verification. But the message was not actually from Apple, and the link in it redirected people to a bogus site that captured their login credentials. Eventually, the hackers were able to leak 100 TB of data, causing an estimated loss of almost $100 million.
This is just one case of many where malicious actors impersonate legitimate entities to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information. Such an attack can only cause monetary loss but also damage an organization’s reputation.
The good news is that spam, phishing, and malware can all be prevented by using strong email security solutions and measures. It’s time to see how.
Crafting a Secure Email Ecosystem: 10 Practices to Uphold
Enterprise email security can involve filtering incoming and outgoing emails, encryption measures, domain-based message authentication, and much more. Here are ten essential email security practices that can help you prevent a phishing attack and keep malicious emails at bay.
1. Strong Passwords
One of the best ways to protect your email account is to use complex, unique passwords (follow this password checklist). This means avoiding (at all costs!) anything that can be easy to guess, such as names, birthdays, common words, or number sequences like 123456.
The best passwords use passphrases or a combination of various letters (lowercase and uppercase), numbers, and symbols. Many businesses choose to use a password management solution that doesn’t just generate these secure keywords but also takes care of auto-filling and updating them and gives IT teams the power to manage permissions.
2. Secure Email Gateways
A secure email gateway can filter incoming and outgoing emails. These tools know how to look for threats like phishing attacks, spam, and malware and block the malicious links before they reach the user. What’s more, secure email gateways can also automatically encrypt outgoing emails (more on this below) to prevent sensitive data from leaving your organization.
Gateways can be deployed on-premises or as a cloud service, depending on your business needs. For example, a secure email gateway can be a better option if you already use a cloud-based email system like Microsoft 365.
3. 2FA (Two-Factor Authentication)
Two-factor Authentication (or 2FA) is another excellent option for ensuring a password is not easily crackable. You’ve probably come across this technology already. For instance, when you are required to give a website a number sent to your mobile phone. Without this second piece of information, you are simply not allowed to log in.

Many email services come with 2FA already. Some good email security examples include Google and Apple, both of which have them on their accounts. If you’re using a different provider, you can check to see whether adding 2FA is a viable option.
Hackers will have a lot more trouble accessing your email accounts if you indeed use Two-factor Authentication.
4. Encrypted Connections
Your emails can potentially be intercepted in transit, even if you use password-protected networks. However, by encrypting your messages, you can ensure whoever sees it can’t actually read it.
How?
By scrambling the data into a secret code, you can only unscramble it if you know a unique digital signature key.
Many email services support encryption protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security). Their goal is to protect the transmission of your emails. So, when possible, ensure that your email client or app is configured to use secure connections when sending and receiving emails.
5. Regular Backups
Another best practice for enterprise email security is regularly backing up your messages to a secure location. This makes it possible to recover important information if your email is compromised. Now, you shouldn’t just back up your email content but also your contacts, settings, and any important attachments.
The best backup option is a different server or an external hard drive. The idea is to have the files somewhere else that is not your computer in the immediate context you use daily. Many businesses, in fact, prefer to use cloud-based systems that automatically detect any changes and make a backup of them.
6. Security Awareness Training
Another essential good practice is to educate yourself and your organization about email security and common phishing tactics. For example, you can conduct regular security awareness training to teach employees how to recognize and respond to phishing attempts.
These are some of the most common emails that can result in breaches:
- Phishing emails: Messages that look legitimate (and often include logos and signatures that help in this perception). For example, emails from supposed banks or companies your business uses frequently.
- Spoof emails: Messages that seem to come from someone you personally know (but are actually from hackers).
- Spear phishing emails: Highly targeted messages that are designed to attack a specific victim (for example, someone in the management team).
Another essential component of dangerous emails is the link they often include. Any training should always cover the importance of understanding when a link is suspicious and the risks of downloading attachments that can be of a vulnerable type (such as .exe files).
7. Antivirus Software and Regular Updates
One of the ways in which hackers can access your emails is through outdated antivirus programs. They know they can leverage certain weaknesses and try to steal information that way. So, no matter which software you use, you should always make sure you enable automatic updates for it (this should apply both to the operating system and any programs you use).
Another thing to keep in mind is that many antivirus solutions support active scanning. This can be a good way to ensure you detect any viruses or malware as soon as it reaches your system.
8. Email Proxies
Email proxies, also known as email relay services or SMTP proxies, are also part of email security best practices for employees. They act as intermediary servers for sending and receiving emails. In other words, they are a sort of middleman between the sender’s email client or server and the recipient’s.
One of the advantages of using an email proxy is that users can maintain their privacy by masking their original IP address. This can be useful when individuals or organizations want to send emails without revealing their geographic location or network details. Some proxies also offer IP rotation, so you can switch between IP addresses. What’s more relevant, though, is that email proxies can analyze email content, including links and attachments, for known phishing indicators.
9. Incident Response Planning
Incident Response Planning (also known as IRP) is a crucial part of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy, too. So, what is it? It’s a structured approach to preparing for, managing, and mitigating the impact of security incidents and breaches.
There are roughly three phases to incident response planning:
- Preparation: Organizations establish a team of experts in IT, legal, compliance, and public relations who create detailed documentation, including an incident response plan, policy, and a list of critical assets.
- Detection: The team implements real-time monitoring and intrusion detection email security tools to identify any unusual or suspicious activities. They also set up custom alerts and triggers to notify the incident response team when potential incidents are detected.
- Containment: Once an incident is confirmed, immediate action is taken to isolate affected systems or networks to prevent the spread of the threat.
- Recovery: This last phase involves restoring affected systems and data from clean backups and any security improvements and measures to prevent similar incidents in the future.
10. Password Management Software
Password management software is designed to help you securely store, generate, and manage your passwords. In other words, these solutions offer a convenient and secure way to handle the multitude of login credentials that people need to use as part of their business activities.
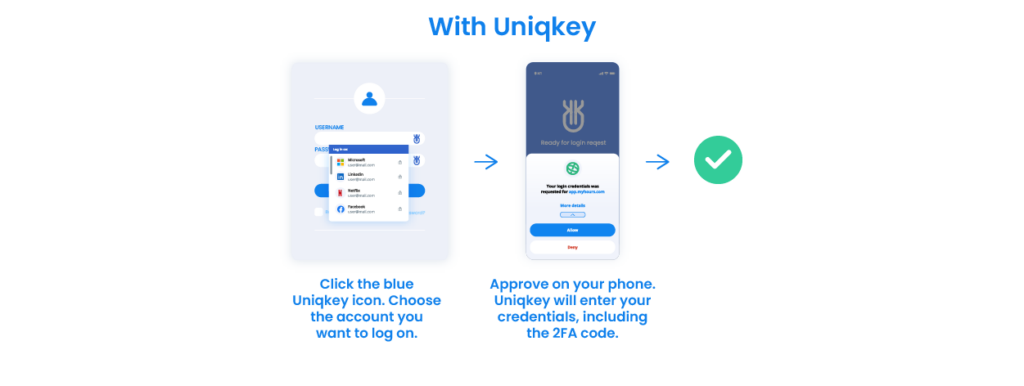
For example, password managers like Uniqkey create centralized management for employee access rights and protect every point for more security. These programs can also automate password use by creating, storing, and sharing passwords that follow the best practices (including 2FA).
A password management solution helps with onboarding and termination, too. When someone joins or leaves the company, you can instantly add or remove access – all while complying with essential regulations and data security standards.
Conclusion
Maintaining solid enterprise email security best practices is essential for preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data. Measures like strong passwords, two-factor authentication, email encryption, anti-phishing solutions, and employee training have all been proven to enhance security.
If you want to simplify your management and reduce the risk of your email communications being intercepted, check out Uniqkey. Our solution is designed to help businesses and enterprises adopt secure password habits. Schedule a demo today to learn more about the Uniqkey platform.


