It is well-documented that organisations face significant risks from insider threats or threats posed by employees, contractors, or business associates. According to the Breach Level Index, in fact, 40% of the publicly reported data breaches in 2016 resulted from malicious insider activity. However, even as the risk of insider threats rises, most companies and organisations are not prepared to detect or mitigate them.
There is little doubt our businesses increasingly rely on digital infrastructure. So, in this guide, we will delve into the process of identifying, understanding, and safeguarding against insider threats. From recognizing red flags to implementing proactive measures, we will explain how to fortify your organisation’s defences and protect against the often overlooked risks that lurk within.
In this article…
What is an Insider Threat?
An insider threat refers to the potential risk and harm that arises from individuals within an organisation – who may exploit their privileged access to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of sensitive information, systems, or networks. Thus, they can pose a significant security risk due to their proximity and familiarity with the organisation’s internal workings.
Insider threats primarily originate from people who, by virtue of their association with an organisation, possess a level of access and familiarity with its internal workings. This group typically includes:
- Employees: Internal staff members, ranging from entry-level employees to executives, are integral to the daily operations of an organisation. Their access to sensitive information and systems, coupled with their knowledge of internal processes, makes them potential sources of insider threats.
- Contractors: External entities engaged by an organisation to provide specialized services, such as IT support, maintenance, or project-based work, fall under the category of contractors. While their contributions are valuable, the temporary nature of their association may pose challenges in ensuring the same level of commitment to security protocols.
- Business Associates: Individuals or entities with a professional association with the organisation, such as vendors, suppliers, or partners, can also present insider threat risks. Their proximity to sensitive data or critical systems, often necessitated by collaboration requirements, underscores the need for vigilance in managing these external relationships.
Types of Insider Threats
Insider threats can be classified into three main types: accidental, malicious, or compromised. Let’s look at each of them in some more detail.
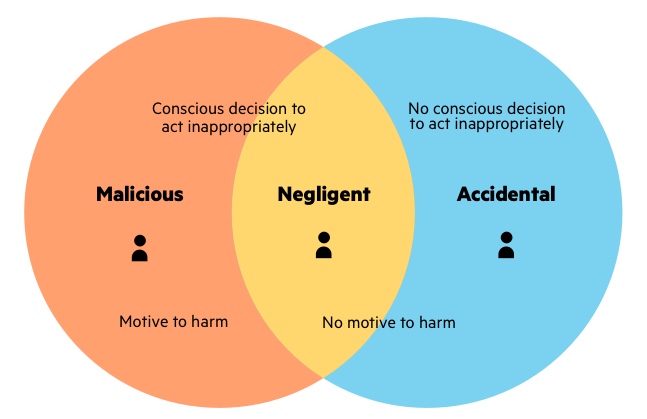
Accidental or Negligent Insiders
When we talk about accidental insider threats, we specifically refer to the possibility of an employee contributing to a security breach without knowing it. This can happen due to a lapse in judgment, no security monitoring, or a human error resulting from a lack of training.
Accidental threats typically stem from well-intentioned but inadvertent actions by employees or individuals. Let’s see an accidental cyber security insider threat example. An employee falls victim to a phishing email or a message that appears from a well-known source (like a bank or service provider) but includes a malicious link. The person inadvertently clicks on the link. Then, he or she mistakenly shares sensitive information with unauthorized parties.
Malicious Insiders
The main differentiator for malicious insiders is an intentional purpose. In other words, malicious insiders deliberately aim to cause harm to the organization. This can be done, for instance, through the theft of sensitive data, sabotage, or intentionally compromising systems.
A malicious insider can be a dissatisfied employee, disgruntled former staff, or someone seeking personal gain through unauthorized access to sensitive information. Now, it’s essential to remember that malicious insider threats can bypass security measures due to their associated legitimate and privileged access. So, they are particularly challenging to detect and prevent.
Compromised Insiders
Compromised insider threats are those in which individuals’ credentials or access rights have been compromised or exploited by external entities. The thing is, though, these individuals might have their accounts hijacked through phishing attacks, social engineering, or other malicious tactics – and they do not know it.
Just as it happens with the other types of threats, though, once their access is compromised, threat actors can exploit their privileges to gain unauthorized entry or perform malicious activities within the organization’s systems.
How to Identify an Insider Threat
Because a possible insider threat originates from people who have legitimate credentials, it can be quite difficult to pinpoint suspicious activity. Now, while it’s challenging to pinpoint every potential threat, there are several strategies you can employ to enhance your organisation’s ability to detect these risks.
One way to identify insider threat indicators involves recognizing unusual or suspicious behaviour that may suggest a potential risk. For example:
- Employees accessing systems or sensitive data during non-business hours or at times inconsistent with their regular work patterns.
- Frequent requests for elevated privileges, access to sensitive information, or attempts to bypass normal authorization processes.
- Unusual or large-scale transfers of sensitive data to external devices, cloud services, or personal email accounts.
- Repeated failed login attempts, especially if they involve unauthorised access attempts or probing of system vulnerabilities.
- Irregular patterns in network traffic, such as unusual data transfers, access to restricted areas, or communication with known malicious IP addresses.
- Drastic changes in behaviour, attitude, or work performance may indicate personal or professional issues.
- The use of unauthorised devices, such as USB drives or external hard disks, for data storage or transfer.
- Repeated violations of security policies, such as sharing passwords, using unapproved applications, or attempting to disable security measures.
- Expressions of discontent, resentment, or signs of job dissatisfaction that may lead to malicious actions.
- Suspicious alterations to or gaps in audit logs could be an attempt to cover up unauthorised activities.
It’s important to note that these indicators should be considered in the broader context of an organisation’s operations, and not every instance may be indicative of malicious intent.
Best Practices to Detect Insider Threats Quickly
From leveraging advanced technological solutions to fostering a culture of vigilance, there are many proactive measures you can take that may make the crucial difference in staying one step ahead of potential risks within the organisational fold. We can classify these into three main categories.
Technological Solutions:
- User Activity Monitoring: Implement comprehensive tools to track employees’ actions on the network, systems, and applications.
- Behavioural Analytics: Utilise analytics to establish baseline behaviour and detect anomalies in user activity.
- Access Controls and Privilege Management: Enforce the principle of least privilege and regularly review access controls.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions: Monitor and control the movement of sensitive data.
- Endpoint Security: Strengthen security on individual devices with antivirus software, firewalls, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implement automated tools to monitor network traffic, system logs, and user activities.
Employee Training and Awareness:
- Educate employees about security policies, the importance of protecting sensitive information, and the potential consequences of insider threats.
- Foster a culture of security awareness to empower employees to recognize and report suspicious activities.
Organisational and Procedural Measures:
- Incident Response Plans: Develop and test incident response plans specific to insider threats.
- Periodic Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify vulnerabilities and ensure effective security controls.
- Collaboration Between Departments: Foster collaboration between IT security, human resources, and management to share information about employee behaviour.
- Insider Threat Programs: Establish dedicated teams or personnel responsible for monitoring, analysing, and responding to potential insider threats.
How to Prevent Insider Threats
Preventing insider threats requires a comprehensive and proactive approach that combines technological measures (such as access control, monitoring, and detection), organisational policies, and cultural and organisational measures.
Access Control and Privilege Management
Least Privilege Access: This approach involves granting employees the minimum level of access required for their specific job responsibilities. By limiting access to sensitive information or critical systems, organisations can significantly reduce the potential for unauthorised actions. Regularly reviewing and updating access permissions based on employees’ roles within the organisation also ensures that access remains aligned with current job responsibilities.
User Training and Awareness: Access control extends beyond technical measures; it encompasses the human factor as well. Educating employees about security policies and the importance of protecting sensitive information is a pivotal component of access control and privilege management. Regular training sessions instil a culture of security awareness, empowering employees to understand their role in safeguarding organisational assets.
Implement Robust Onboarding and Offboarding Processes: Effective access control begins at the onboarding stage and continues throughout an employee’s tenure. Robust onboarding and offboarding processes ensure that employees receive the appropriate access permissions upon joining the organisation and have them promptly revoked upon departure or role changes.
Monitoring and Detection
User Behaviour Monitoring: Advanced analytics and monitoring tools establish baseline behaviour for users, enabling the identification of anomalies that may indicate potential risks. By continuously analysing patterns in user activity, your organisation can swiftly detect deviations from the norm, allowing for timely intervention and investigation.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Solutions: Implementing DLP solutions is crucial in preventing the unauthorised transfer or sharing of sensitive data. These solutions monitor and detect unusual data activities, enforcing policies related to data protection. By setting up preventive measures, organisations can significantly mitigate the risk of insider threats aimed at exfiltrating critical information.
Endpoint Security: Securing endpoints is paramount in preventing insider threats that may originate from individual devices. Endpoint security, including antivirus software, firewalls, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, adds an extra layer of defence. Regular updates and patching further fortify these endpoints against potential vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of insider-initiated security breaches.
Cultural and Organisational Measures
Insider Threat Programs: Establishing insider threat programs or dedicated teams is a strategic organisational measure that serves insider threat detection perfectly. These security teams specialise in behavioural analysis, conducting investigations into suspicious activities and potential threats originating from within the organisation.
Encourage Reporting: Fostering a culture where employees feel empowered to report concerns is essential, too. For instance, establishing anonymous reporting channels provides a safe space for employees to share information about potential insider threats without fear of retaliation. Encouraging open communication contributes to collective vigilance, enabling organisations to act swiftly upon receiving reports of suspicious activities.
Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits and assessments is a systemic approach to maintaining a secure environment. These audits identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security controls remain effective against emerging threats. By continuously reviewing and updating security policies based on the evolving threat landscape, organisations create a resilient foundation for preventing insider threats.
Conclusion: Combating Shadow IT
Insider threats can manifest across various sectors and industries, and their detection and prevention pose significant challenges for organisations aiming to safeguard their assets and maintain trust. Effectively addressing insider threats requires a multifaceted approach, combining technological solutions, robust security policies, and employee awareness programs to mitigate the risk posed by individuals within the organisation.
Uniqkey is an all-in-one platform designed to protect companies against increasing cyber threats, including insider risks. Uniqkey’s intuitive password manager empowers employees and shifts the burden of secure password practices away from the user and onto an automated system, promoting safer habits without demanding significant behavioural changes. The platform also streamlines access management by offering centralised control of your organisation’s digital infrastructure, making it easier to ensure the integrity of your company’s digital assets.
Here are some ways in which Uniqkey can help your company with insider threat prevention and your overall security strategy:
- Centralised Access Management: By centralising access management, Uniqkey allows organisations to monitor and control who has access to sensitive data, reducing the likelihood of unauthorised access or internal threats.
- User-Friendly Password Management: Uniqkey offers an intuitive password manager that empowers employees and promotes safer habits without demanding significant behavioural changes, thus addressing the human-centred challenges posed by insider threats.
- Controlled Access Permissions: The platform enables organisations to easily grant specific access to selected users and groups, ensuring that only the right people have access to the right data.
- Rapid Adjustment to Access Permissions: Uniqkey allows for swift adjustments to access permissions, mitigating risk in emergencies and helping to address potential insider threat incidents.
- Military-Grade Encryption and Compliance: Uniqkey secures data at rest and in transit using military-grade encryption and is 100% GDPR compliant, thus providing a robust security framework to prevent insider threats.
🏆Contact us to get your 14-day free trial and start combating shadow IT today.

