HOTP (HMAC-based One-time Password) and TOTP (Time-based One-time Password) are both forms of one-time authentication methods that generate unique codes used for secure logins, with different approaches to generating one-time passwords. However, they differ in the way they utilize a “moving factor” to generate these codes.
This post will make a detailed comparison between the two authentication methods. Before getting into that it’s important to establish the basic principles of two-factor authentication.
Table of contents
A brief overview of 2FA or 2-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security measure that adds an extra layer of protection to password-protected online accounts.
It can be thought of as a two-step verification process that involves
Something you know: Typically a password
Something you have: A code sent via SMS or an authenticator application/ hardware key that you plug into the computer/ a fingerprint scan or facial ID.
Authenticator apps, such as Google Authenticator and Authy, are commonly used to generate these codes, providing an additional layer of security.
When a user tries to log into a 2FA-enabled online account by entering the login credentials (username and password) the server sends a code or prompt to verify the second authenticating factor. The login process is completed only when both factors are verified.
If a hacker steals the username and password for a 2FA-enabled account, they won’t be able to log in without the second factor. 2FA makes it much harder for hackers to gain unauthorized access to online accounts.
There are many forms of 2FA authentication. HOTP and TOTP are both examples of such authentication methods.
Understanding One-Time Passwords (OTPs)
One-Time Passwords (OTPs) are a crucial component of multi-factor authentication (MFA), adding an extra layer of security beyond the traditional username and password combination. Unlike static passwords, OTPs are designed to be used only once, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. These passwords are typically generated by an authenticator app or a hardware token and can be sent to the user via SMS, email, or a mobile app.
The generation of OTPs relies on a shared secret key between the user and the server. When a user attempts to log in, they enter their username and password, after which the OTP is generated using the shared secret key and a moving factor, such as a counter or time. The OTP is then sent to the user, who must enter it to complete the authentication process.
OTPs are widely adopted across various industries, including finance, healthcare, and e-commerce, to ensure secure access to sensitive information and systems. They are also prevalent in consumer-facing applications like online banking and social media, providing an additional layer of security for users. By leveraging OTPs, organizations can enhance their security process and protect against unauthorized access.
What is an HOTP one time password?
HOTP stands for HMAC-based One-Time Password. HMAC stands for Hash-based message authentication code. HMAC works like a digital fingerprint that ensures that A. the message is not tampered with during transmission and B. the message has come from the authorized source.
The authentication server maintains the counter value, ensuring that each one-time password is unique and valid for a specific instance.
So, HOTP is a one-time password based on the HMAC algorithm.
How is HOTP generated?
HMAC-based OTP is generated using a secret key and a counter.
The secret key has a constant value shared by the user and the server. The counter starts at an initial value and is incremented with each attempt to generate a code.
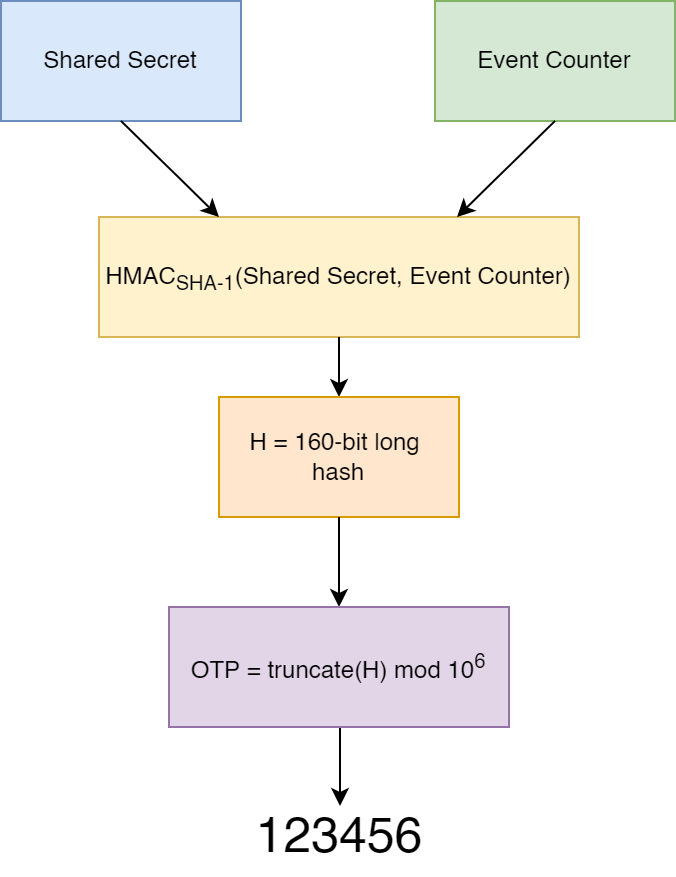
Fig. HOTP working explained
The secret and the counter are combined and put through a hash function to generate a hash at the user’s end. The OTP is a truncated version of this hash. This truncated hash is shared by the user with the server. The server uses the same secret, counter, and hash function to verify that the right code is sent by the user. With every attempt the counter changes and so does the hash. This ensures that an older code cannot be reused.
Synchronization between both the server and the user’s device is crucial to ensure the correct counter value is used for generating the OTP.
The success of HOTP depends on server-client synchronization.
What is a TOTP time based otp?
TOTP stands for Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP), where time works as a changing factor to ensure old passwords cannot be reused. This method is an improvement on the HMAC-based OTP. Instead of a counter that shifts with every attempt, it uses a counter that shifts with time.
How does a TOTP work?
Each TOTP stays valid for a certain period. This period is called a time step. It is usually set at 30 seconds and can be modified in some cases. The user and the server use the same clock to determine the current time.
For TOTP to work effectively, synchronization between both the server and the user’s device is essential to ensure the correct time value is used.
The current time is usually represented by the number of seconds elapsed since January 1, 1970. The current time is then divided by the time step to find out the current time value. That means the time value changes with each passing time step.
Now, the secret key shared by the client/user and the server along with the time value is put through an HMAC algorithm from the user’s end. A truncated version of the resultant hash works as the OTP. The same process is repeated by the server to verify the authenticity of the TOTP sent by the user.
TOTP is an improvement on HOTP and they have certain common elements. But there is a lot that segregates TOTP and HOTP in terms of the process, security, usability, and application. The following sections will walk you through some of those differences.
| Features | HOTP | TOTP |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithm Basis | HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) | HMAC (Hash-based Message Authentication Code) |
| Key Aspect | Counter-based | Time-based |
| Primary Usage | OTPs are generated based on a counter value | OTPs are generated based on the current time |
| Security | Relies on the security of the counter value; if compromised, OTPs can be predicted | Relies on time synchronization; less prone to prediction if the time source is secure |
| Synchronization Requirement | Synchronization of the counter between server and client is crucial | Synchronization of time between server and client is crucial |
| OTP Validity | OTP validity is not time-bound and depends on the counter increment | OTP is valid for a short period, typically 30 to 60 seconds |
| Implementation Complexity | Less complex as it requires simple counter-management | More complex due to the need for time synchronization |
| User Experience | Users can use the OTP until the next one is generated | Time-bound OTP can be more challenging for users, leading to a need for quick entry |
| Risk of Replay Attacks | Lower, as each OTP is based on the next counter value | Higher, as OTPs are valid for a set time period |
| Standard References | Defined in RFC 4226 | Defined in RFC 6238 |
| Typical Applications | Suitable for systems where time synchronization is challenging | Preferred in online systems where time synchronization is feasible |
| User Cases | Less complex as it requires simple counter-management | Better for infrequent events and transaction authentication due to the event-based nature |
| Token Required | A hardware or software token is required to generate the passwords | A hardware or software token is required to generate the passwords |
| Password Reuse | The same password may repeat after the validity window elapses making it less secure | Better for frequent events and session authentication due to the time-based nature |
The Moving Factor in HOTP vs TOTP
The moving factor is what ensures that each OTP is unique. It creates the primary difference between HOTP and TOTP.
The moving factor in HOTP: The moving factor in HOTP is a counter that increments with each generated code. That means one code loses validity only when the next one is generated.
The moving factor in TOTP: The moving factor in TOTP is the time value calculated by dividing the time-based since January 1, 1970, by the time step. Therefore, the moving factor changes automatically with every time step (30/60/90 seconds).
Synchronization between client and server
Synchronization between both the server and the user’s device is essential for a one-time password to work. Or else the server would get the moving factor wrong and fail to authenticate the legitimate user.
Client-server synchronization in HOTP
HOTP uses a turn-based counter as the moving factor to generate the OTP. The counter value entered from the client’s end needs to match that of the server for successful authentication. This can pose a minor challenge in the event of a connectivity issue.
Let’s say, a user generates an OTP with the counter value 0 and doesn’t share it with the server. And then generates another OTP with the counter value 1 and shares it with the server. The server should try to verify the code by using the counter value 0. In such an event, the process would fail. The server is usually programmed to try 3 to 5 subsequent OTP to authenticate a user to avoid that.
Client-server synchronization in TOTP
In the case of TOTP, synchronization takes place through device time. It is independent of network connectivity or instance of attempts. Both the user’s OTP token and the server keep generating new codes with every time step, Since both sides follow the current Unix time, they’re always in sync.
TOTP vs HOTP: Security
The biggest flaw in the HMAC-based one-time password is that the validation window is indefinite. One OTP is valid until the next is generated. This creates some security challenges.
Replay attacks
If a man-in-the-middle attacker gets access to the HOTP as it is transmitted, they can reuse it to gain unauthorized access to the user’s account.
The chances of replay attacks are extremely low in the case of TOTPs as the small time step ensures the rapid regeneration of authentication codes.
Phishing attacks
HOTP-based authentication is less vulnerable to phishing attempts since it is mostly done using hardware tokens like key fobs. However, if the token gets stolen, it can cause severe problems.
Hackers can acquire the TOTP through phishing websites. Hackers can manipulate users into entering their credentials to log into a service account by putting up a duplicate site. They can relay the information to the legitimate site. The server will ask for the 2FA information, which the user will enter into the fake site. Hackers can hijack the online account just like that.
Since time-based OTP changes every 30 seconds, hackers have very little time to run the whole process of stealing accounts.
User experience
Both HOTP and TOTP can work offline. Both are easy to set up and use. However, TOTP gets the upper hand here since it doesn’t require the user to manually advance their counter.
Authenticator apps, such as Google Authenticator, are widely used to generate TOTPs, providing a user-friendly and secure method for two-factor authentication.
Some users may find that entering a TOTP within the time step is a challenge, but it is this challenge that adds security to the method. TOTP is also easier to implement.
The use of HOTP doesn’t require a device with a clock that is synced with the server. In the case of a TOTP, the need for a clock for OTP authentication necessitates an additional communication device such as a smartphone.
Also, TOTP requires a digital authenticator app such as Google authenticator to function. Nevertheless, these dependencies are not considered cons since they add security to the process.
Supported Authenticator App Applications
One Time Password TOTP is among the most popular authentication methods supported by a wide array of online services. Time-based OTPs are among the most popular authentication methods supported by a wide array of online services. HOTP, on the other hand, is more suitable for hardware token-based authentication. Hence, the use of HOTP is waning.
Key Differences: HOTP vs TOTP
HOTP (Hash-Based One-Time Password) and TOTP (Time-Based One-Time Password) are two prominent OTP algorithms used in multi-factor authentication. Both algorithms utilize a shared secret key and a moving factor to generate OTPs, but they differ significantly in their approach.
HOTP employs a counter as the moving factor, which increments with each authentication attempt. The counter value, combined with the shared secret key, generates the OTP. However, HOTP is more vulnerable to security concerns, such as replay attacks, because the counter value can be intercepted and reused by attackers.
In contrast, TOTP uses time as the moving factor. The current time, combined with the shared secret key, generates the OTP. TOTP is inherently more secure than HOTP because the time-based OTP is valid only for a short period, typically 30 to 60 seconds. This limited validity window makes it more challenging for attackers to intercept and reuse the OTP, thereby enhancing the overall security of the authentication process.
Choosing the Right Algorithm for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate algorithm between HOTP and TOTP depends on your specific security requirements and user experience considerations. If your primary concern is security and minimizing the risk of replay attacks, TOTP is likely the better choice. Its time-based nature ensures that OTPs are valid only for a brief period, making it difficult for attackers to exploit.
However, if you require a more flexible solution that can function in offline environments, HOTP may be more suitable. HOTP allows users to enter the OTP at any time, without the constraints of a time window, which can be more user-friendly in certain scenarios.
User experience is another critical factor. TOTP requires users to enter the OTP within a specific time frame, which can be challenging for some. In contrast, HOTP offers more flexibility, allowing users to enter the OTP at their convenience. Evaluating these factors will help you choose the algorithm that best meets your needs.
Implementation and Deployment Considerations
When implementing and deploying OTPs, several key considerations must be addressed to ensure a secure and user-friendly experience. First, selecting a robust shared secret key is crucial. The key should be complex and difficult for attackers to guess or intercept.
Secure generation and transmission of OTPs are also vital. Use encryption and secure communication protocols to protect the OTP during transmission. Additionally, consider the user experience by providing clear instructions on how to use the OTP, including offering backup codes in case the user loses access to their authenticator app or hardware token.
Regularly reviewing and updating your OTP implementation is essential to maintain security and compliance with industry standards. Monitor for potential security concerns, such as replay attacks, and update the shared secret key and moving factor as needed. By addressing these considerations, you can ensure a robust and secure OTP implementation that enhances the overall security of your authentication process.
Bottomline
TOTP codes change every 30 seconds and HOTP code changes with every attempt. TOTP brings an additional layer of security in the form of time. The same cannot be said for HOTP.
A wide array of service providers including password management tools like Uniqkey have adopted the TOTP. It is definitely less hackable than the HOTP, which means more security and reliability. Both methods are effective in generating one-time passwords that enhance security and reliability for various applications.